website
|
Start Page News Sites |
Digitale Stad Eindhoven |

|
|
| This Site's Pages |
| Home |
| Who's who? |
| Myths, Facts and Fallacies |
| About Zeolites |
| China |
| Software |
| Other Sites |
| The Free Software Foundation |
| The GNU Free Softare Project |
| Scepticism on the Web |
| On-line Chinese Tools |
| Midi Music Sites |
| the BachWorks |
| Harpsichordist to the Internet |
| Organ / Jeux soundfont |
| Harpsichord / Hpschd soundfont |
| Email Us |
| Jos van Wolput & Jin Yuehua |

|

|

|
| © 2004 - 2021 |
| Jos van Wolput |
Zeolites, catalysis, Brønsted and Lewis site acidity, FTIR, ESR
Zeolites are microporous crystalline solids with well-defined structures. Generally they contain silicon, aluminium and oxygen in their framework and cations, water and/or other molecules within their pores.Many occur naturally as minerals, and are extensively mined in many parts of the world. Others are synthetic, and are made commercially for specific uses, or produced by research scientists trying to understand more about their chemistry.
Zeolites have the ability to act as catalysts for chemical reactions which take place within the internal cavities.
Major uses are in petroleum refining and chemical process industries, ion-exchange (water softening and purification), and in the separation and removal of gases and solvents.
They are often also referred to as molecular sieves.
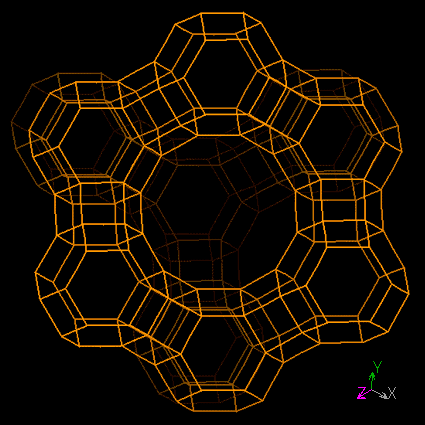
|
Explore the following websites for more information on zeolites:Wikipedia: ZeolitesWhat are Zeolites ? The Zeolite Group of Minerals Zeolite Catalysts and Sieves Zeolite Structures Characterization by IR spectroscopy Growing zeolite crystals in space: A Zeal for Zeolites |
an 'artist impression' of a catalytic reaction |
 |
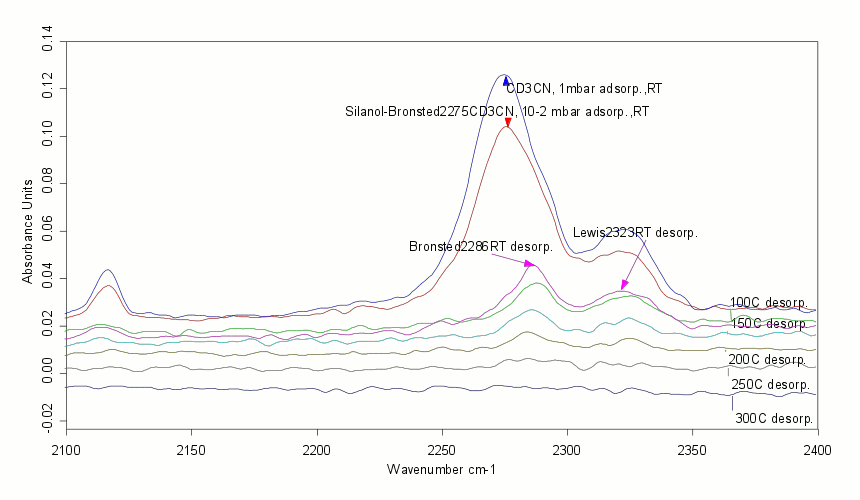
FTIR spectrum of adsorbed deuterated acetonitrile on a zeolite showing Brønsted and Lewis acid sites. |
|
